1.3 Exercises on solving systems of linear equations: matrix inversion and Cramer's rule
- Use Cramer's rule to find the values of x and y that solve the following two equations simultaneously.
3x − 2 y = 11 2x + y = 12 We haveandx = 
11 −2 
12 1 / 
3 −2 
2 1 = 5 y = 
3 11 
2 12 / 
3 −2 
2 1 = 2. - Solve the two equations in the previous problem by using matrix inversion.
Solution is
(1/7) 
1 2 
−2 3 
11 
12 = 
5 
2 - Use Cramer's rule to find the values of x, y, and z that solve the following three equations simultaneously.
4x + 3 y − 2 z = 7 x + y = 5 3x + z = 4 We haveandx = 
7 3 −2 
5 1 0 4 0 1 / 
4 3 −2 
1 1 0 3 0 1 = 0 andy = 
4 7 −2 
1 5 0 3 4 1 / 
4 3 −2 
1 1 0 3 0 1 = 5 z = 
4 3 7 
1 1 5 3 0 4 / 
4 3 −2 
1 1 0 3 0 1 = 4 - Solve the three equations in the previous problem by using matrix inversion.
Solution is
(1/7) 
1 −3 2 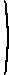
−1 10 −2 −3 9 1 
7 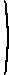
5 4 = 
0 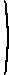
5 4