3.2.3 Exercises on quadratic forms: conditions for semidefiniteness
- Determine whether each of the following quadratic forms in two variables is positive or negative definite or semidefinite, or indefinite.
- x2 + 2xy.
- −x2 + 4xy − 4y2
- −x2 + 2xy − 3y2.
- 4x2 + 8xy + 5y2.
- −x2 + xy − 3y2.
- x2 − 6xy + 9y2.
- 4x2 − y2.
- (1/2)x2 − xy + (1/4)y2.
- 6xy − 9y2 − x2.
- The matrix is
The determinant is −1 < 0, so the quadratic form is indefinite.

1 1 
1 0 . - The matrix is
The first-order principal minors are −1 and −4; the determinant is 0. Thus the quadratic form is negative semidefinite (but not negative definite, because of the zero determinant).

−1 2 
2 −4 . - The matrix is
the leading principal minors are −1 and 2, so the quadratic form is negative definite.

−1 1 
1 −3 ; - The associated matrix is
The leading principal minors are 4 > 0 and (4)(5) − (4)(4) = 4 > 0. Thus the matrix is positive definite.

4 4 
4 5 . - The associated matrix is
The leading principal minors are −1 < 0 and (−1)(−3) − (1/2)(1/2) > 0. Thus the matrix is negative definite.

−1 1/2 
1/2 −3 . - The associated matrix is
The principal minors are 1 > 0, 9 > 0, and (1)(9) − (−3)(−3) = 0. Thus the matrix is positive semidefinite.

1 −3 
−3 9 . - The associated matrix is
The determinant is −4 < 0. Thus the matrix is indefinite.

4 0 
0 −1 . - The associated matrix is
The determinant is (1/2)(1/4) − (−1/2)(−1/2) < 0. Thus the matrix is indefinite.

1/2 −1/2 
−1/2 1/4 . - The associated matrix is
The principal minors are −1 < 0, −9 < 0, and (−1)(−9) − (3)(3) = 0. Thus the matrix is negative semidefinite.

−1 3 
3 −9 .
- Determine whether each of the following quadratic forms in three variables is positive or negative definite or semidefinite, or indefinite.
- −x2 − y2 − 2z2 + 2xy
- x2 − 2xy + xz + 2yz + 2z2 + 3zx
- −4x2 − y2 + 4xz − 2z2 + 2yz
- −x2 − y2 + 2xz + 4yz + 2z2
- −x2 + 2xy − 2y2 + 2xz − 5z2 + 2yz
- y2 + xy + 2xz
- −3x2 + 2xy − y2 + 4yz − 8z2
- 2x2 + 2xy + 2y2 + 4z2
- The matrix is
The first-order minors are −1, −1 and −2, the second-order minors are 0, 2, and 2, and the determinant is 0. Thus the matrix is negative semidefinite.

−1 1 0 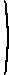
1 −1 0 0 0 −2 . - The matrix is
The first-order principal minors are 1, 0, and 2, so the only possibility is that the quadratic form is positive semidefinite. However, the first second-order principal minor is −1. So the matrix is indefinite.

1 −1 2 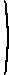
−1 0 1 2 1 2 . - The matrix is
The first-order principal minors are −4, −1, and −2; the second-order principal minors are 4, 4, and 1, and the third-order principal minor is 0. Thus the matrix is negative semidefinite.

−4 0 2 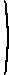
0 −1 1 2 1 −2 . - The matrix is
The leading principal minors are −1, 1, and 7, so the quadratic form is indefinite.

−1 0 1 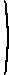
0 −1 2 1 2 2 . - The matrix is
The leading principal minors are −1, 1, and 0, so the matrix is not positive or negative definite, but may be negative semidefinite. The first order principal minors are −1, −2, and −5; the second-order principal minors are 1, 4, and 9; the third-order principal minor is 0. Thus the matrix is negative semidefinite.

−1 1 1 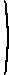
1 −2 1 1 1 −5 . - The matrix is
Thus the form is indefinite: one of the first-order principal minors is positive, but the second-order one that is obtained by deleting the third row and column of the matrix is negative.

0 1/2 1 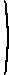
1/2 1 0 1 0 0 . - The matrix is
with leading principal minors −3, 2, and −4. So the form is negative definite.

−3 1 0 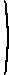
1 −1 2 0 2 −8 , - The matrix is
The leading principal minors are 2, 3, and (2)(8) − (1)(4) = 12 > 0. Thus the matrix is positive definite.

2 1 0 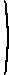
1 2 0 0 0 4 .
- Consider the quadratic form 2x2 + 2xz + 2ayz + 2z2, where a is a constant. Determine the definiteness of this quadratic form for each possible value of a.
The matrix isThe first-order minors are 2, 0, and 2, the second-order minors are 0, 3, and −a2, and determinant −2a2. Thus for a = 0 the matrix is positive semidefinite, and for other values of a the matrix is indefinite.

2 0 1 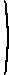
0 0 a 1 a 2 . - Determine the values of a for which the quadratic form x2 + 2axy + 2xz + z2 is positive definite, negative definite, positive semidefinite, negative semidefinite, and indefinite.
The matrix isThe leading principal minors are 1, −a2, and −a2.

1 a 1 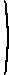
a 0 0 1 0 1 . Thus if a ≠ 0 the matrix is indefinite.
If a = 0, we need to examine all the principal minors to determine whether the matrix is positive semidefinite. In this case, the first-order principal minors are 1, 0, and 1; the second-order principal minors are 0, 0, and 0; and the third-order principal minor is 0. Thus the quadratic form is positive semidefinite.
Conclusion: If a ≠ 0 the matrix is indefinite; if a = 0 it is positive semidefinite.
- Consider the matrix
Find conditions on a and b under which this matrix is negative definite, negative semidefinite, positive definite, positive semidefinite, and indefinite. (There may be no values of a and b for which the matrix satisfies some of these conditions.)

a 1 b 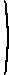
1 −1 0 b 0 −2 . The matrix is not positive definite or positive semidefinite for any values of a and b, because two of the first-order principal minors are negative. Necessary and sufficient conditions for it to be negative definite are- a < 0
- −a − 1 > 0, or a < −1 (looking at first second-order principal minor)
- 2a + 2 + b2 < 0 (looking at determinant).
It is negative semidefinite if and only if a ≤ −1, −2a − b2 ≥ 0, and 2a + 2 + b2 ≤ 0. The second condition implies the first, so the matrix is negative semidefinite if and only if a ≤ −1 and 2a + 2 + b2 ≤ 0.
Otherwise the matrix is indefinite.
- Show that the matrix
is not positive definite.

1 0 1 1 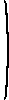
0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 The second order principal minor obtained by deleting the second and fourth rows and columns is 0, so the matrix is not positive definite. (Alternatively, the third-order leading principal minor is 0, and the principal minor obtained by deleting the second and third rows and columns is 0.)